What are the traditional types of investments made by a life insurance company?
Insurance companies tend to invest most of the premium in bonds, and the rest in stocks, mortgages, and liquid short-term investments. Bonds, stocks, and mortgage instruments comprise around 90 percent of investments for life insurance companies, and over 80 percent of those for property and casualty insurers. Among the top three asset classes are bonds, which include corporate bonds, municipal bonds, US government bonds and foreign government bonds. Followed by liquid short-term investments and cash is the fourth largest asset class. Insurance companies also invest in derivatives, contract loans, securities lending, real estate, and preferred stock. All the minor investments are meant to add diversity for risk management
What are reasons for life insurance companies entering into venture capital?
Life insurance companies prefer to invest the premiums for two reasons: increasing the profits for more stable money sources, and possibly lowering its premium amount for more clients. While most insurance companies invest mostly in bonds, stocks and mortgages, life insurance companies have been taking a more active role in recent years, and even establishing their own venture capital divisions.
The motivations for life insurance companies entering into venture capital can be primarily attributed to the following three reasons.
- Increasing balance for life insurance companies but decreased traditional investable targets. As more emergent companies focused on cutting edge technologies, such as big data and artificial intelligence start to stand out in the globe, there is no reason for life insurance companies not to invest in this promising industry. Especially in the time of COVID-19, while traditional companies are more severely affected and struggling for transformation, those innovative companies relying more on technology are able to adapt and survive in the current situation.
- The prevailing market trend in the growth of corporate venture capital.
- Strategic benefits from investment in venture capital. By investing in tech companies in early stages, traditional life insurance companies can acquire and combine novel technologies for their use.
What are examples of global life insurance companies having VC divisions?
Among those venture capital arms of mature life insurance companies, the majority of them are in the United States and the European Union. Insurance-related investment, VCs of mature life insurance shows common preference in investing in software, IT and FinTech industries. The chart below provides an overview with the corporate venture capital divisions of leading life insurance companies, with a basic description of their strategy, companies and industries they invested in.
| Name | Location | Description | Companies Invested | Industries Invested |
| AXA Venture Partners | France | AXA Venture Partners is a venture capital fund investing in high-growth,
technology-enabled companies. |
NS8; Contrast Security; Block Stream | Software; HealthCare; IT |
| MassMutual Ventures | US | MassMutual Ventures (MMV) is the venture capital arm of MassMutual. | Payfone; IEX Group; Digital Guardian | Software; IT; Cyber Security |
| Kaiser Permanente Ventures | US | Kaiser Permanente Ventures is a
California-based corporate venture capital firm investing in healthcare companies. |
Freenome; Valeritas; Health Catalyst | HealthCare; Medical Device; Medical |
| Northwestern Mutual Future Ventures | US | Life insurance provider Northwestern Mutual’s investment arm. | Chime; OJO Labs; Ladder | FinTech; Financial Service; Insurance |
| Nationwide Ventures | US | Nationwide Ventures, corporate venture arm of Nationwide Insurance | Nexar; Vesta Healthcare; Upstream Security | Insurance; Software; Insurtech |
| Munich Re Ventures | Germany | Munich Re Ventures is the strategic venture capital arm of Munich Re. | Next Insurance; Bought by Many; Hippo Insurance | Insurance; IT; InsurTech |
| American Family Ventures | US | American Family Ventures is the venture capital branch of American Family Insurance | Hometap; Clearcover; CoverHound | Insurance; InsurTech; Finance |
| Transamerica Ventures | US | Transamerica Ventures provides seed, venture, and growth-stage funding to innovators in the FinTech, enterprise IT, and Internet sectors. | Auxmoney;
CipherCloud; H2O.ai |
Fintech; InsurTech; Analytics |
| Cigna Ventures | US | Cigna Ventures is the corporate venture arm of Cigna, that accelerates growth of startups in the healthcare industry. | Omada Health; arcadia.io; GNS Healthcare | HealthCare; Medical; IT |
| New York Life Ventures | US | New York Life Ventures NYLIC is the largest mutual life-insurance company in the United States. | Trifacta; Carrot;
Cogito Corporation |
HealthCare; Machine Learning; Software |
| Allianz X | Germany | Allianz X is the digital investment unit of the Allianz Group that invests in digital growth companies related to insurance. | Gojek; Amwell; N26 | Financial Service; Automotive; FinTech |
Source: Crunchbase
We are going to analyze investment motivation and strategies by taking a closer look at two life insurers, representative of relatively different backgrounds.
- Kaiser Permanente Ventures (KPV)
Kaiser Permanente Ventures, a US-based venture capital arm of Kaiser Permanente, is dedicated to partnering with entrepreneurs to advance clinical quality, service, and affordability. The Permanente Federation is the national leadership and consulting organization for the eight Permanente Medical Groups, which are composed of nearly 23,000 physicians who care for 12.2 million Kaiser Permanente members. Affiliated to Kaiser Permanente, KPV has 20 years of venture capital investing experience, with more than $500 million under management.
Source: crunchbase
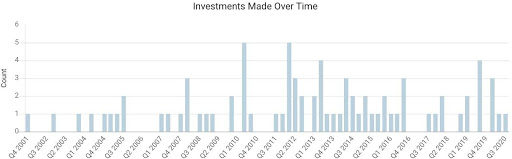
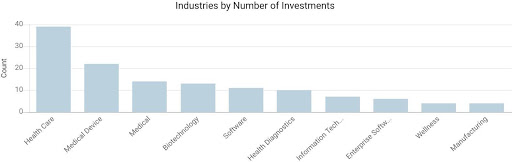
Starting from 2001, KPV has engaged in 80 investments, among which 12 are leading investments, ranked top by the number of investments in our list. We can see in the graph that KPV accelerated its pace for VC investment from 2010. The firm invests in the health care sector primarily in the United States with a focus on health information technology, digital health, health care services, medical devices, diagnostics, and precision medicine.
Top three companies that received the most funding from KPV are:
- $160M in Freenome: a platform that helps design healthy conditions for an individual based on their cell-free genome
- $150M in Valeritas: the developer of V-GO, a disposable insulin pump, and a micro needle patch for the treatment of Type 2 diabetes
- $85M in Health Catalyst: a tech platform that organizes and links health-related data from different systems and makes it available for all users
All three companies represent important innovations in healthcare delivery. Through these VC investments, Kaiser Permanente is able to obtain insights from close engagement with these entrepreneurs and build better on their products for high-quality, accessible, and cost-effective care in the United States.
- AXA Venture Partners (AVP)
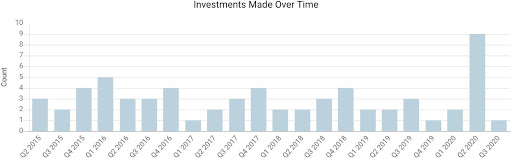
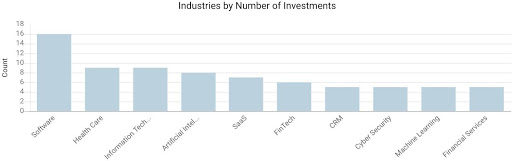
Based in France, AXA Venture Partners, the venture arm of AXA Group, is a VC fund investing in high-growth technology-enabled companies. Though relatively later launched when compared to KPV, AVP has been continuously investing in 65 companies over only 5 years, making it an inactive insurer-backed VC fund. The firm, managing $800 million, invests in enterprise software and disruptive technology such as digital security, consumer technologies, fintech, and insure-tech.
Source: crunchbase
Top three companies that received the most funding from AXA Venture Partners are:
- $123M in NS8: a fraud prevention platform that combines behavioral analytics and real-time scoring to help businesses minimize risk
- $65M in Contrast Security: automatically detects vulnerabilities and defends against targeted attacks and bots with self-protecting software
- $55M in Blockstream: the global leader in Bitcoin & blockchain technology, making financial markets more efficient by reducing reliance on trust
The above three all suggest AVP’s strong orientation on online security technologies and succeed in setting the company’s major investment themes on cyber risk, digital healthcare, FinTech, and Insure-tech. The primary objective of the fund is not only about a return on investment, but also a synergy for strategic impact on AXA’s business initiatives.




